# Lab 3 - Integrating an app
In this laboratory, we will learn how to modify our application in order to work with Istio. For that purpose, we will use the Online Boutique (opens new window) a sample microservices application provided by Google.

While integrating an application with Istio, we must following these simple steps:
- Deploy in Kubernetes our services injected with Istio sidecards.
- Deploy Istio networking services to K8s for the services with our custom rules and configuration.
# 1. Downloading microservices-demo application
git clone git@github.com:GoogleCloudPlatform/microservices-demo.git
git reset --hard v0.2.1
cd microservices-demo
# 2. Testing microservices-demo application without Istio
Disable istio-injection:
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=disabled --overwriteDeploy the application:
kubectl apply -f ./release/kubernetes-manifests.yamlRun to see pods are in a Ready state and wait until all pods have all pods instances
READYandSTATUSin Running:kubectl get podsOpen application to outside traffic:
kubectl port-forward deployment/frontend 18080:8080Open the Online Boutique (opens new window) in your browser.
Destroy the deployment.
kubectl delete -f ./release/kubernetes-manifests.yaml
Errors while setting up microservices-demo
Sometimes, this demo application has several problems when you deploy it into Kubernetes.
If you have waited too much time, try destroying the deployment and launching it again.
# 3. Injecting Istio sidecar into the application
Istio helps developers while integrating their apps into the service mesh. It is as easy as executing istioctl kube-inject command for the application manifest:
istioctl kube-inject -f ./release/kubernetes-manifests.yaml
Now, check a single service in order to see the current changes made by istioctl:
Default K8s deployment specification:
--- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: checkoutservice spec: selector: matchLabels: app: checkoutservice template: metadata: labels: app: checkoutservice spec: containers: - name: server image: gcr.io/google-samples/microservices-demo/checkoutservice:v0.2.0 ports: - containerPort: 5050 readinessProbe: exec: command: ["/bin/grpc_health_probe", "-addr=:5050"] livenessProbe: exec: command: ["/bin/grpc_health_probe", "-addr=:5050"] env: - name: PORT value: "5050" - name: PRODUCT_CATALOG_SERVICE_ADDR value: "productcatalogservice:3550" - name: SHIPPING_SERVICE_ADDR value: "shippingservice:50051" - name: PAYMENT_SERVICE_ADDR value: "paymentservice:50051" - name: EMAIL_SERVICE_ADDR value: "emailservice:5000" - name: CURRENCY_SERVICE_ADDR value: "currencyservice:7000" - name: CART_SERVICE_ADDR value: "cartservice:7070" # - name: DISABLE_STATS # value: "1" # - name: DISABLE_TRACING # value: "1" # - name: DISABLE_PROFILER # value: "1" # - name: JAEGER_SERVICE_ADDR # value: "jaeger-collector:14268" resources: requests: cpu: 100m memory: 64Mi limits: cpu: 200m memory: 128MiSpecification injected with the sidecard:
--- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: checkoutservice spec: selector: matchLabels: app: checkoutservice strategy: {} template: metadata: annotations: prometheus.io/path: /stats/prometheus prometheus.io/port: "15020" prometheus.io/scrape: "true" sidecar.istio.io/status: '{"version":"e2cb9d4837cda9584fd272bfa1f348525bcaacfadb7e9b9efbd21a3bb44ad7a1","initContainers":["istio-init"],"containers":["istio-proxy"],"volumes":["istio-envoy","istio-data","istio-podinfo","istio-token","istiod-ca-cert"],"imagePullSecrets":null}' creationTimestamp: null labels: app: checkoutservice istio.io/rev: "" security.istio.io/tlsMode: istio service.istio.io/canonical-name: checkoutservice service.istio.io/canonical-revision: latest spec: containers: - env: - name: PORT value: "5050" - name: PRODUCT_CATALOG_SERVICE_ADDR value: productcatalogservice:3550 - name: SHIPPING_SERVICE_ADDR value: shippingservice:50051 - name: PAYMENT_SERVICE_ADDR value: paymentservice:50051 - name: EMAIL_SERVICE_ADDR value: emailservice:5000 - name: CURRENCY_SERVICE_ADDR value: currencyservice:7000 - name: CART_SERVICE_ADDR value: cartservice:7070 image: gcr.io/google-samples/microservices-demo/checkoutservice:v0.2.1 livenessProbe: exec: command: - /bin/grpc_health_probe - -addr=:5050 name: server ports: - containerPort: 5050 readinessProbe: exec: command: - /bin/grpc_health_probe - -addr=:5050 resources: limits: cpu: 200m memory: 128Mi requests: cpu: 100m memory: 64Mi - args: - proxy - sidecar - --domain - $(POD_NAMESPACE).svc.cluster.local - --serviceCluster - checkoutservice.$(POD_NAMESPACE) - --proxyLogLevel=warning - --proxyComponentLogLevel=misc:error - --concurrency - "2" env: - name: JWT_POLICY value: third-party-jwt - name: PILOT_CERT_PROVIDER value: istiod - name: CA_ADDR value: istiod.istio-system.svc:15012 - name: POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.name - name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.namespace - name: INSTANCE_IP valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: status.podIP - name: SERVICE_ACCOUNT valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName - name: HOST_IP valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: status.hostIP - name: CANONICAL_SERVICE valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.labels['service.istio.io/canonical-name'] - name: CANONICAL_REVISION valueFrom: fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.labels['service.istio.io/canonical-revision'] - name: PROXY_CONFIG value: | {"proxyMetadata":{"DNS_AGENT":""}} - name: ISTIO_META_POD_PORTS value: |- [ {"containerPort":5050} ] - name: ISTIO_META_APP_CONTAINERS value: server - name: ISTIO_META_CLUSTER_ID value: Kubernetes - name: ISTIO_META_INTERCEPTION_MODE value: REDIRECT - name: ISTIO_META_WORKLOAD_NAME value: checkoutservice - name: ISTIO_META_OWNER value: kubernetes://apis/apps/v1/namespaces/default/deployments/checkoutservice - name: ISTIO_META_MESH_ID value: cluster.local - name: TRUST_DOMAIN value: cluster.local - name: DNS_AGENT image: docker.io/istio/proxyv2:1.8.1 imagePullPolicy: Always name: istio-proxy ports: - containerPort: 15090 name: http-envoy-prom protocol: TCP readinessProbe: failureThreshold: 30 httpGet: path: /healthz/ready port: 15021 initialDelaySeconds: 1 periodSeconds: 2 timeoutSeconds: 3 resources: limits: cpu: "2" memory: 1Gi requests: cpu: 10m memory: 40Mi securityContext: allowPrivilegeEscalation: false capabilities: drop: - ALL privileged: false readOnlyRootFilesystem: true runAsGroup: 1337 runAsNonRoot: true runAsUser: 1337 volumeMounts: - mountPath: /var/run/secrets/istio name: istiod-ca-cert - mountPath: /var/lib/istio/data name: istio-data - mountPath: /etc/istio/proxy name: istio-envoy - mountPath: /var/run/secrets/tokens name: istio-token - mountPath: /etc/istio/pod name: istio-podinfo initContainers: - args: - istio-iptables - -p - "15001" - -z - "15006" - -u - "1337" - -m - REDIRECT - -i - "*" - -x - "" - -b - "*" - -d - 15090,15021,15020 env: - name: DNS_AGENT image: docker.io/istio/proxyv2:1.8.1 imagePullPolicy: Always name: istio-init resources: limits: cpu: "2" memory: 1Gi requests: cpu: 10m memory: 40Mi securityContext: allowPrivilegeEscalation: false capabilities: add: - NET_ADMIN - NET_RAW drop: - ALL privileged: false readOnlyRootFilesystem: false runAsGroup: 0 runAsNonRoot: false runAsUser: 0 securityContext: fsGroup: 1337 serviceAccountName: default volumes: - emptyDir: medium: Memory name: istio-envoy - emptyDir: {} name: istio-data - downwardAPI: items: - fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.labels path: labels - fieldRef: fieldPath: metadata.annotations path: annotations name: istio-podinfo - name: istio-token projected: sources: - serviceAccountToken: audience: istio-ca expirationSeconds: 43200 path: istio-token - configMap: name: istio-ca-root-cert name: istiod-ca-cert status: {}
As you can see, the service is modified deeply adding a lot new stuff. Next, We will learn what Istio does.
# 4. Sidecar injection
In simple terms, sidecar injection is adding the configuration of additional containers to the pod template. The added containers needed for the Istio service mesh are:
istio-init This init container is used to setup the iptables rules so that inbound/outbound traffic will go through the sidecar proxy. An init container is different than an app container in following ways:
- It runs before an app container is started and it always runs to completion.
- If there are many init containers, each should complete with success before the next container is started.
So, you can see how this type of container is perfect for a set-up or initialization job which does not need to be a part of the actual application container. In this case, istio-init does just that and sets up the iptables rules.
istio-proxy This is the actual sidecar proxy (based on Envoy).
# 4.1 Automatic injection
Most of the times, you don’t want to manually inject a sidecar every time you deploy an application, using the istioctl command, but would prefer that Istio automatically inject the sidecar to your pod. This is the recommended approach and for it to work, all you need to do is to label the namespace where you are deploying the app with istio-injection=enabled.
Once labeled, Istio injects the sidecar automatically for any pod you deploy in that namespace. In the following example, the sidecar gets automatically injected in the deployed pods in the istio-dev namespace.
# 5. Deploying microservices-demo with Istio
Deploy the application:
istioctl kube-inject -f ./release/kubernetes-manifests.yaml | kubectl apply -f -Run to see pods are in a Ready state:
kubectl get pods
# 6. Adding external HTTPS connectivity through Istio
Istio by default is high secure, so no connectivity is added if you do not say so. Now, we will deploy a new manifest adding connectivity services through Istio:
istio-micro-services-networking.yaml:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: Gateway metadata: name: frontend-gateway spec: selector: istio: ingressgateway # use Istio default gateway implementation servers: - port: number: 80 name: http protocol: HTTP hosts: - "*" - port: number: 443 name: https protocol: HTTPS tls: mode: SIMPLE credentialName: microservices-demo-credential # must be the same as secret hosts: - microservices-demo.example.com --- apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: frontend-ingress spec: hosts: - "*" gateways: - frontend-gateway http: - route: - destination: host: frontend port: number: 80 --- apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: frontend spec: hosts: - "frontend.default.svc.cluster.local" http: - route: - destination: host: frontend port: number: 80 --- apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: ServiceEntry metadata: name: whitelist-egress-googleapis spec: hosts: - "accounts.google.com" # Used to get token - "*.googleapis.com" ports: - number: 80 protocol: HTTP name: http - number: 443 protocol: HTTPS name: https --- apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: ServiceEntry metadata: name: whitelist-egress-google-metadata spec: hosts: - metadata.google.internal addresses: - 169.254.169.254 # GCE metadata server ports: - number: 80 name: http protocol: HTTP - number: 443 name: https protocol: HTTPS ---
Download istio-micro-services-networking.yaml.
Create certificate for the gateway and its custom domain:
openssl req -x509 -sha256 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -subj '/O=example Inc./CN=example.com' -keyout example.com.key -out example.com.crt openssl req -out microservices-demo.example.com.csr -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout microservices-demo.example.com.key -subj "/CN=microservices-demo.example.com/O=microservices-demo organization" openssl x509 -req -days 365 -CA example.com.crt -CAkey example.com.key -set_serial 0 -in microservices-demo.example.com.csr -out microservices-demo.example.com.crtUpload certificate to kubernetes:
kubectl create -n istio-system secret tls microservices-demo-credential --key=microservices-demo.example.com.key --cert=microservices-demo.example.com.crtDeploy necessary gateway, ingress and egress services for the application:
kubectl apply -f istio-micro-services-networking.yamlEnsure that there are no issues with the configuration:
istioctl analyze
# 6.1 Determining the application URL
As in the previous laboratory, we will have to obtain the URL for accessing the application:
Obtain host and ports:
export INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(.name=="http2")].nodePort}') export SECURE_INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(.name=="https")].nodePort}') export INGRESS_HOST=$(minikube ip) export GATEWAY_URL=microservices-demo.example.com:$SECURE_INGRESS_PORTAdd
microservices-demo.example.comto/etc/hosts:sudo bash -c "echo '$INGRESS_HOST microservices-demo.example.com ' >> /etc/hosts"Run the following command to retrieve the external address of the application.
echo https://"$GATEWAY_URL"Access the app using precious URL:
# 7. Checking services using the Istio dashboard
Now, it is time to visually review what is deployed in Istio:
Access the Kiali dashboard. The default user name is
adminand default password isadmin.istioctl dashboard kialiIn the left navigation menu, select Graph and in the Namespace drop down, select default.
The Kiali dashboard shows an overview of your mesh with the relationships between the services in the
Microservices Demosample application. It also provides filters to visualize the traffic flow.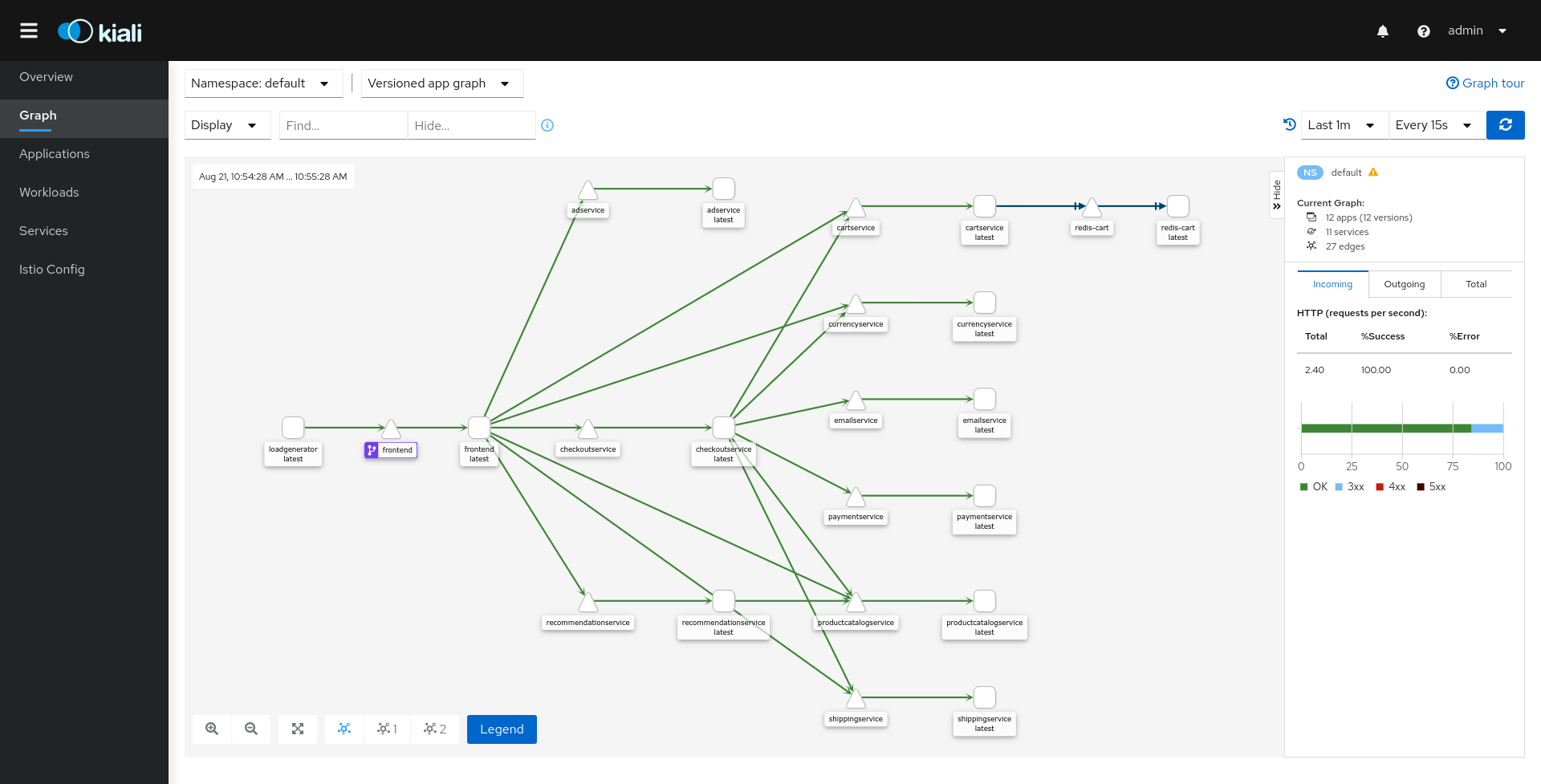
# 8. Removing resources
Remove line that contains
microservices-demo.example.comin/etc/hosts:sudo sed -i '/microservices-demo.example.com/d' /etc/hostsRemove created resources:
kubectl delete -f istio-micro-services-networking.yaml istioctl kube-inject -f ./release/kubernetes-manifests.yaml | kubectl delete -f -
